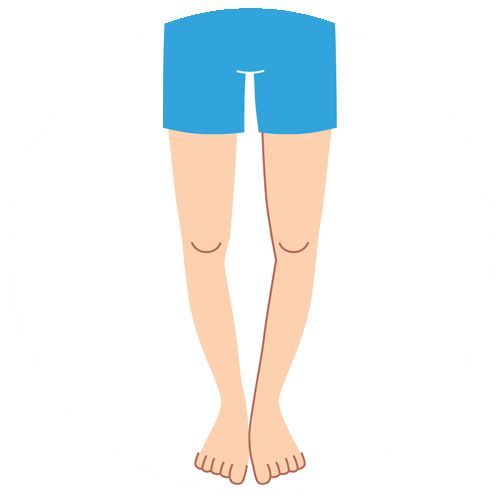
Each infant is born bowlegged as he remained in mother’s womb in a folded position. Hence, bow legs are considered normal in children whose age is less than 18 months. As the child starts walking, his legs get straightened gradually. But bow legs are considered as a physical deformity if it is present when the child is about 3 years old. As a form of physical deformity, bow legs or genu varum is marked by bowing of the child’s lower leg in relation to his thigh.

Bow legs may be caused due to a variety of illnesses. Normally, the physical deformity is caused due to abnormal development of bones or fractures that have not healed properly. However, bow legs are also caused due to Blount’s disease, or lead or fluoride poisoning. Sometimes the physical deformity is caused due to rickets, an illness caused due to lack of Vitamin D.
The parents can identify the physical deformity based on a number of symptoms. They can know if the child is bowlegged when his knees to not touch while standing with both feet together. Also, a bowlegged child can bow his symmetrically on both sides of his body. The parents must avail the assistance of a seasoned orthopaedic immediately if bow legs continue in a child whose age is more than 3 years.
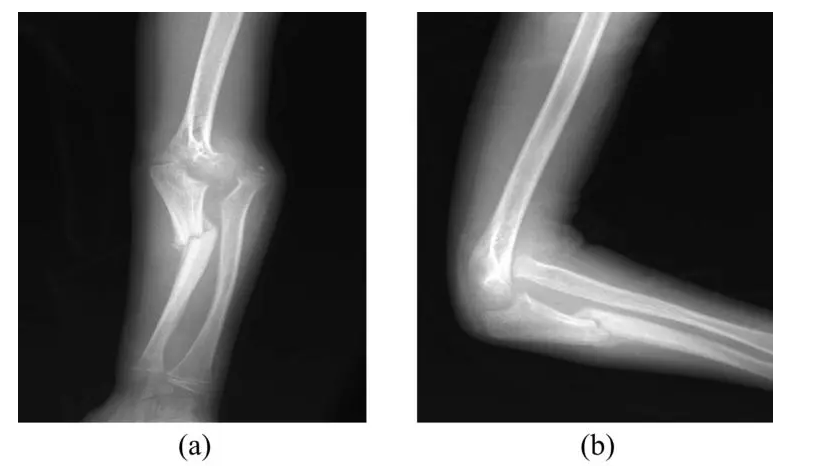
A seasoned child orthopaedic can diagnose bow legs simply by observing the child’s knees. Some healthcare providers even diagnose bow legs by measuring the distance between two knees of the child when he lies on the back. However, the orthopaedic also perform blood test to check if the deformity is caused due to rickets. They even recommend x-rays when the bowing is extreme or based on the test results. But x-ray is recommended only if the child is older than 3 years.
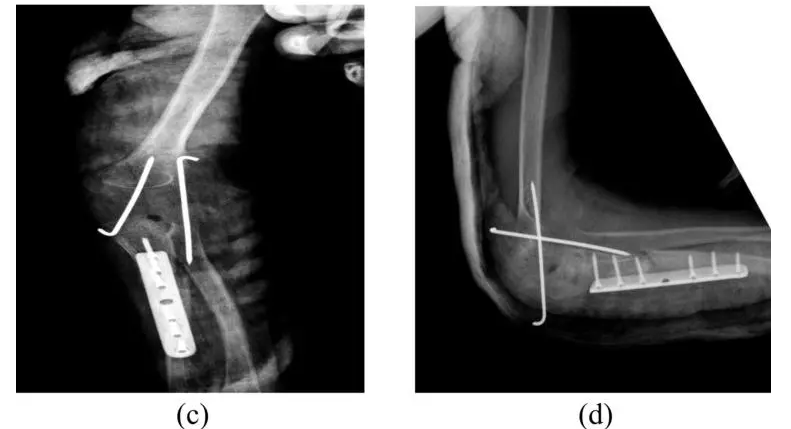
The seasoned orthopaedics monitors the growth of the bow legged child constantly, and observe his knees once in 6 months. Also, they recommend treatment for bowleg only when the child’s condition is extreme. Many orthopaedics treat bow legs through special braces, casts, or shoes. The skilled orthopaedics also corrects the deformity in an adolescent child by performing bow legs surgery. However, the bow legs treatment varies based on the specific condition of each child.
The parents do not have any option to prevent bow legs. Hence, they must avail the assistance of a skilled orthopaedic to monitor the child’s condition and prevent his condition from becoming extreme. The orthopaedic will further recommend the best way to treat bow legs on time and avoid chances of developing arthritis in the knees or hips. Also, the parents must choose a skilled and experienced orthopedic to avail modern treatment, and correct the physical deformity with minimal scar and morbidity.